Coronavirus has everyone staying at their homes due to several lockdowns to contain the spread of infection. The effect of lockdown has been reflecting in several industries like Travel, Retail, IT & several others. One of such industries is the Manufacturing Industry.
In this blog, we would be talking about the importance of the manufacturing industry, the Performance of the Manufacturing industry & the future of the Manufacturing industry.
Importance of the Manufacturing Industry
Even though 60% of the global GDP is contributed by the Service sector, it is heavily dependent on the manufacturing goods for their operation & for their technological progress. For e.g., Facebook & PUBG are pure examples of a service-based industry that generates their revenue by using goods like Desktop & Mobile Phones. According to the World Trade Organization, 80% of interregional trade is in goods, and only 20% is in services.
Stats
- 54% of the Global GDP1 is contributed by 5 countries – US, China, Japan, Germany & India
- 16% of the Global GDP2 is contributed by the manufacturing sector, of which 10% is the share of the Top 5 World Economies.
- The Top 5 World Economies take the majority of share2 (63%) of the Global Manufacturing sector.
Performance of Manufacturing Industry
Over here, we have observed two indicators (Manufacturing PMI3 & Manufacturing Production4) to get an insight on the Performance of the industry – Pre Covid vs. Covid.
Indicators
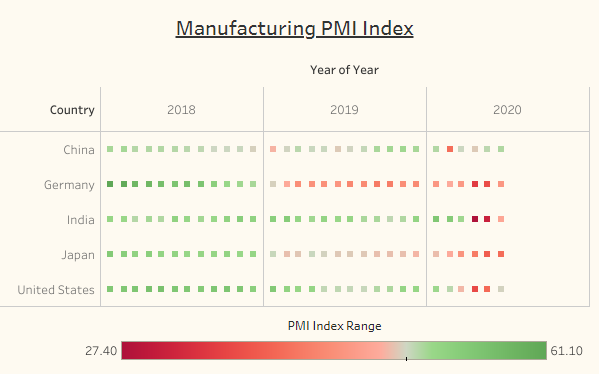
PMI is an indicator of the direction of economic trends in the manufacturing sector. PMI Ranges from 0 to 100, where 50 represents no Change, PMI above 50 represents expansion with respect to the previous month & PMI below 50 represents a contraction compared to the previous month.
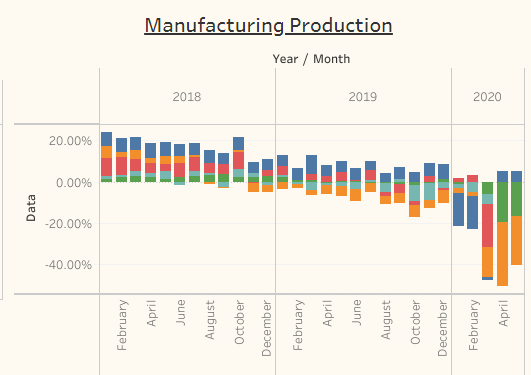
Manufacturing production measures the output of businesses operating in the manufacturing sector.
Few reasons for the declining trend in the manufacturing industry during the Pre-Covid was (i) US-China Trade war (ii) Economic Slowdown (iii) Weakening Demand for manufactured goods
As you can observe, the manufacturing industry in the Top 5 World Economies has been declining since 2018, specifically Germany & Japan. We could also see all the countries except China had faced their major contraction from March 2020. This was due to the lockdown.
In order to understand the revenue impact5 for the manufacturing industry for the year 2020, a survey by ISM was done in May which projects (i) 21.2% decrease in revenue (By 58% of the respondents)
(ii) 10.6% increase in revenue (By 18% of respondents)
(iii) No change in revenue (By 24% of respondents)
Comparing Recessions
Since 2000 the world has seen two major Recessions (i) The Great Recession (ii) The Covid Recession.
These two recessions had different reasons; The Great Recession was caused by the financial crisis & The Covid Recession due to the Pandemic.
While comparing the PMI data between the two recessions,
For the US, China & Germany, the contraction during the Covid-19 Recession was more or less similar to the Great Recession
For Japan, the Covid-19 Recession had contracted less compared to the Great Recession
For India, the Covid-19 Recession had contracted more compared to the Great Recession
Irrespective of the reasons for the Global Recession, the manufacturing industry has contracted.
Manufacturing Industry Recovery
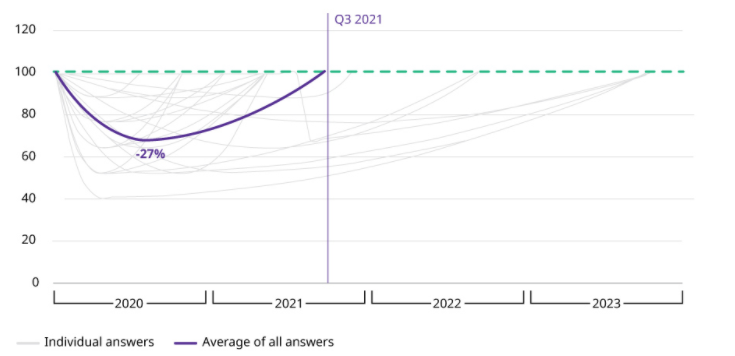
In May, Oliver Wyman6 surveyed top-level executives of globally acting manufacturing firms in the US & they modeled three different Covid scenarios for recovery
V-Shape:
In the “V-shape” scenario, public health measures contain individual outbreaks, and COVID-19 lasts for three to four months. The revenue decline mainly shows in Q2, and the economy recovers quickly in Q3 and Q4.
U-Shape:
In the “U-shape” scenario, the Pandemic will break due to the seasonality of the virus or virus mutation, and COVID-19 will last for a six-to-a year. This would lead to a revenue decline in Q2 and an even more severe decline in Q3 before revenues recover in Q4.
L-Shape:
In the most severe “L-shape” or “financial crisis +” scenario, COVID-19 will last more than 12 months and not be affected by seasonality or hard to fight due to mutation. As a result, the revenue decline would persist throughout four quarters, starting in Q2 2020.
The survey shows that the recovery shape would be U-Shaped with an average decline in revenue by 27%
Future of Manufacturing Industry7
- The Manufacturing industries which opted for early usage of digital technologies will be able to recover faster in this crisis.
- The introduction of data analytics, machine learning, cognitive computing, agile methodologies, omnipresent connectivity, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, blockchain, and additive manufacturing would be widely accepted in the manufacturing sector.
- These Digital Technologies will be the drivers for this industry to be more resilient in the future.