The blog is an introduction for a 3-part series on how additional insights can be gained from your in-house data through process mining to offer competitive advantages.
Organizations have a strong understanding of their critical business processes, such as what is the approach to follow, when it is supposed to happen, who should do what, and under which condition should it be happening, in theory. However, in practice, the actual scenario could be very different from theory, and companies lack the insight to track these dissonances in process steps. Traditional Business Intelligence (BI), web analytics platform, and other statistical tools are not able to detect deviations, bottlenecks, or scrutinize in such cases.
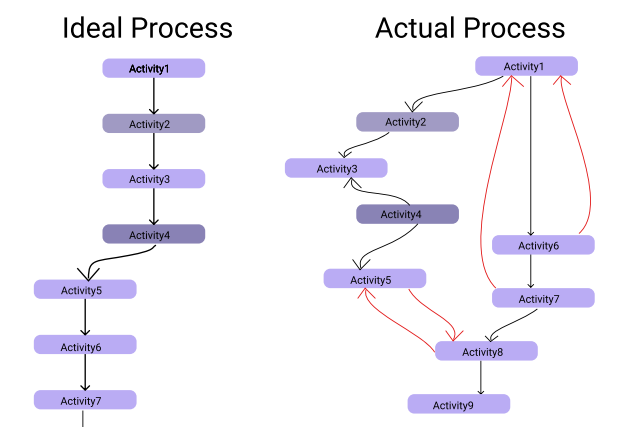
Figure 1- Ideal/Expected process vs. Actual process
Process Mining serves as a new means to improve processes across different clusters. It is an innovative analytical approach that analyzes data from the event logs to gain insights and expose/uncover hidden problems. The event logs help visualize how work is happening, including who did it, the time taken to complete it, and how it departs from the average.
Why is process mining important?
According to market research done by IDC, not only most businesses are unaware of lost potential due to process weaknesses, but they also lose 20-30 percent of their revenue that way.
A company’s ideal process can look very different from that of the actual process. Traditional approaches (annual reviews, employee/customer interviews, workshops, etc.) tend to give a picture very similar to the ideal model but are very far from reality.
Using key performance indicators (KPIs ), process mining identifies where exactly there are opportunities to correct or improve processes.
A few examples of companies that benefited from Process mining (Success Stories)
- Vodafone used process mining and discovered that they have low automated transactions. It resulted in increased purchase orders from 73% to 85%, reduced cost from $3.22/PO to $2.85/PO, and improved time to market by 20%.
- VTB (Russian bank) wanted their processes to be cheaper and faster. Hence they used process mining, and it shortened the throughput time by 30% and, in turn, improved customer satisfaction. It also increased the percentage of timely-handled accounts from 68% to 98%.
- AkzoNobel (Paint manufacturer) missed transparency of what happened in its end-to-end core processes. To overcome this, they used process mining and identified that 18% of processes have manual changes. This led to automation and resulted in cost reduction.
- Veco (Manufacturing company) used Process Mining to reduce the manufacturing lead time of precision parts. It resulted in the reduction of throughput time by 50%.
Process Mining- Features
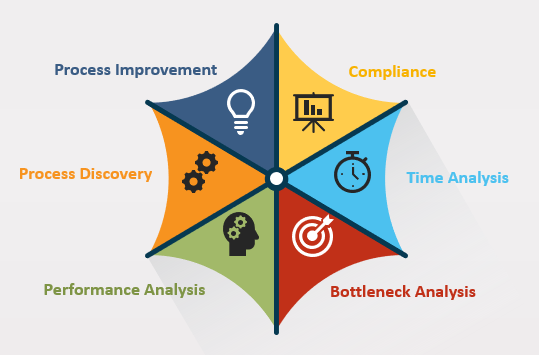
Figure 2- Process mining features
Process Discovery Fact-based understanding of your operations by transforming data to process maps. It helps organizations discover the truth and make better decisions based on the evidence found in the organization’s systems
Compliance Process mining enables an unbiased and fact-based process compliance checking. By discovering and visualizing the actual process and related details, companies gain full transparency of their processes.
Performance Analysis Performance is defined by the efficiency, effectiveness, or success of an event or an entire process. A high number of process variants indicates that the process is non-linear and often has a negative impact on the overall performance.
Bottleneck Analysis A bottleneck describes the scarcity of resources, products or manufacturing materials. A bottleneck delays the processor affects its performance, increasing the throughput time, or even bringing the process to a complete halt.
Time Analysis The duration of the process results from the length of the individual activities, which constitutes a process. ’It’s one of the factors that go into measuring overall process effectiveness and efficiency. A shorter or longer duration may have a positive or negative impact on a process.
Process Improvement Process Improvement involves identifying, analyzing, and improving the existing business processes within an organization for optimization and to meet quality standards.
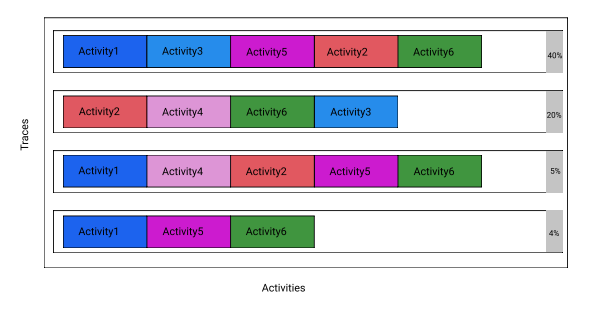
Figure 3- Variants/Traces associated with the same process
Advantages
1) Insights from Raw Data
By reconstructing the process from data already present in the IT systems (event logs), Process Mining allows organizations to diagnose problems based on facts rather than assumptions. This approach eliminates causal and other human errors from the analysis and facilitates structured process improvement.
2) Wide-Range of Applications
Process Mining can be applied for all processes from purchase-to-pay (P2P), order-to-cash (O2C), customer journeys to IT management processes, and in every industry from finance, retail, insurance/banking to logistic services.
3) Fast and Cost-effective
Process Mining reduces the analysis time and minimizes the costs by reducing the number of consultants/analysts.
4) Scalable, Repeatable Analysis
Process Mining connects the knowledge gap that exists between various systems, departments, and functions. The same analysis can be performed again with new data almost without any additional costs.
Conclusion
Manufacturing, sales, insurance, logistics, medicine- all these industries have started exploring the world of process mining. Where there is a digital trace, there is an opportunity for process mining. It has revolutionized how companies extract data and derive actionable insights, but its full potential is yet to be realized. Organizations are now turning to process mining to extract maximum value out of their data. The benefits are faster however accurate insights of the actual processes, speeding up understanding and providing full transparency about the day to day business processes.
In the next blog post of this series, we will discuss how process mining has helped derive more information and insights for a fictitious Smartphone coating company.




